目录
前言
请勿转载,违法必究
英伟达2025年4月论文《Describe Anything: Detailed Localized Image and Video Captioning》https://github.com/NVlabs/describe-anything.git
解决问题:为图像和视频中的特定区域生成详细且准确的描述。
主要贡献:
- 为了解决高质量DLC数据稀缺的问题,我们提出了一个基于半监督学习(SSL)的数据管道(DLC-SDP)
- 创造了用于评估DLC的基准测试DLC-Bench
- 提出了一个为详细局部描述Detailed Localized Captioning (DLC)设计的模型Describe Anything Model(DAM)
注意:DAM是非商用协议,没有公开训练代码和微调方法,所以想“微创新”的就不用看了。
一、研究内容

二、代码解析
2.1 关键代码逻辑
dam\describe_anything_model.py中函数get_description最终调用get_description_from_prompt_iterator函数,构造输入参数:
generation_kwargs = dict(
input_ids=input_ids,
images=image_tensors,
do_sample=True if temperature > 0 else False,
use_cache=True,
stopping_criteria=[stopping_criteria],
streamer=streamer,
temperature=temperature,
top_p=top_p,
num_beams=num_beams,
max_new_tokens=max_new_tokens,
**kwargs
)然后调用DAM模型生成(generate函数)结果:
...
else:
with torch.inference_mode():
output_ids = self.model.generate(**generation_kwargs)
outputs = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
outputs = outputs.strip()
if outputs.endswith(stop_str):
outputs = outputs[: -len(stop_str)]
outputs = outputs.strip()
yield outputs2.2 核心参数解析
核心的输入参数就两个,非常简单:
- input_ids由tokenizer_image_token函数从prompt处理而来。
- image_tensors由get_image_tensor函数从image_pil,mask_pil裁剪而来。
三、模型解析
3.1 视觉大语言模型VILA1.5-3b
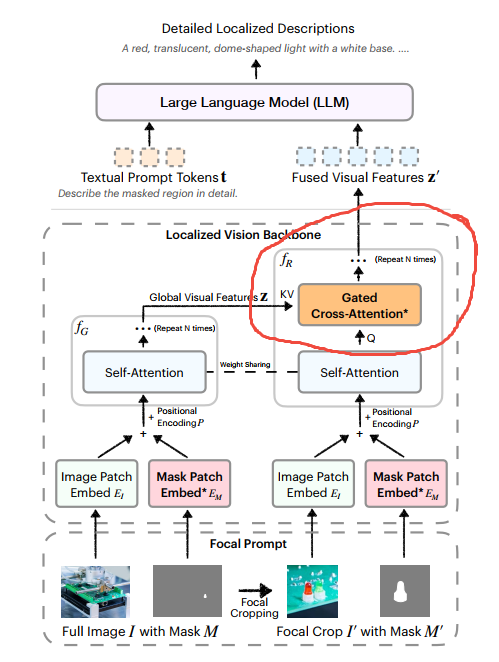
经过分析,DAM nvidia/DAM-3B HuggingFace 依赖英伟达自家的视觉大语言模型 Efficient-Large-Model/VILA1.5-3b HuggingFace,如下图所示:

注意:llm,mm_projector,vision_tower文件夹与英伟达VILA1.5(类似qwen2.5-vl)是完全相同的,这些不属于DAM论文的创新点,大大减少了研究(阅读)的工作量。
VILA1.5 基于LLAVA架构,这里不做延伸学习和深入代码剖析,直接跳过。
3.2 context_provider是DAM的关键创新
dam\model\llava_arch.py中encode_images_with_context函数,核心代码:
# Process the first 4 channels for all images: for image it's the image, for cimage it's the full image
vision_tower = self.get_vision_tower()
# Encode context images (full images)
image_features = vision_tower(images[:, :4, ...]).to(self.device)
# Each cimage has 8 channels (full and crop concatenated), cimage是image with context的缩写
cimage_concatenated = images[cimage_mask]
cimage_full_features = image_features[cimage_mask]
if context_provider.context_provider_type == "cross_attn_end_to_all":
cimage_features = self.context_provider(
cimage_full_features=cimage_full_features,
cimage_concatenated=cimage_concatenated,
vision_tower=vision_tower
).to(self.device)
elif context_provider.context_provider_type == "concat":
# Full features of cimages are computed but not used.
cimage_features = self.context_provider(
cimage_concatenated=cimage_concatenated,
vision_tower=vision_tower
).to(self.device)对应论文中的:
3.3 SAM(SAM2)的功能
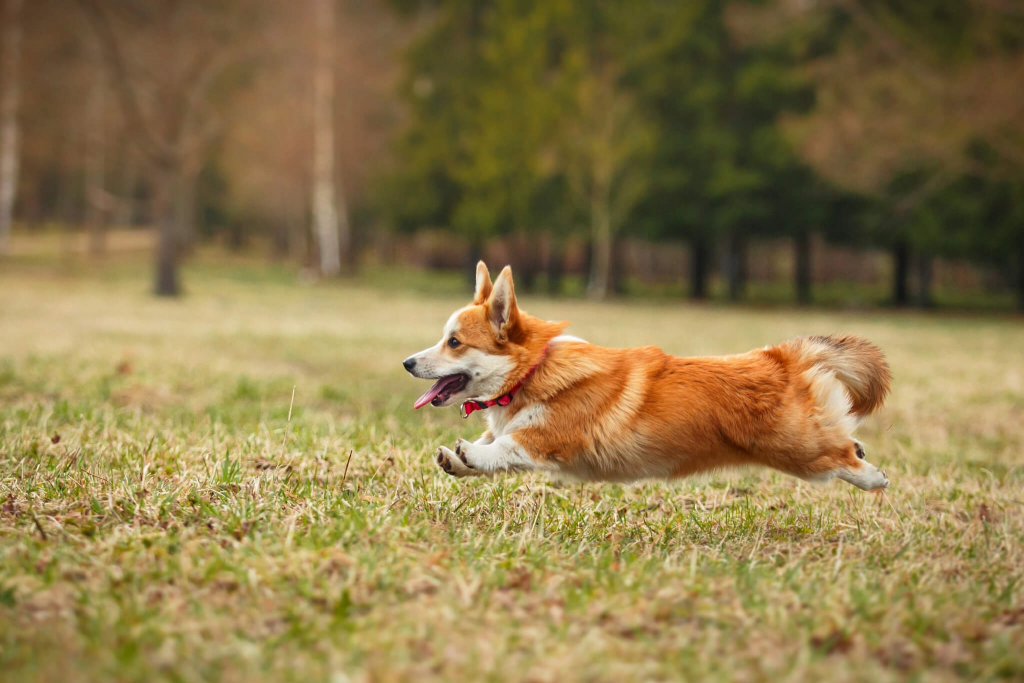
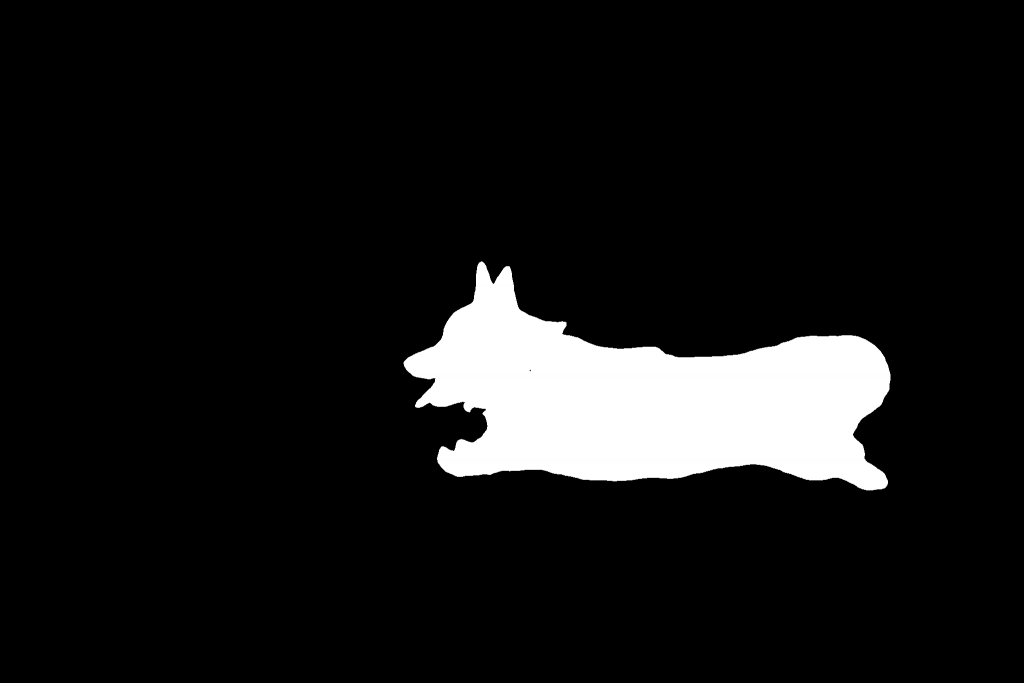
用SAM(SAM2)给DAM做一个遮罩,代表需要DAM模型用文字详细描述的图像区域,例如:

SAM生成的遮罩图:
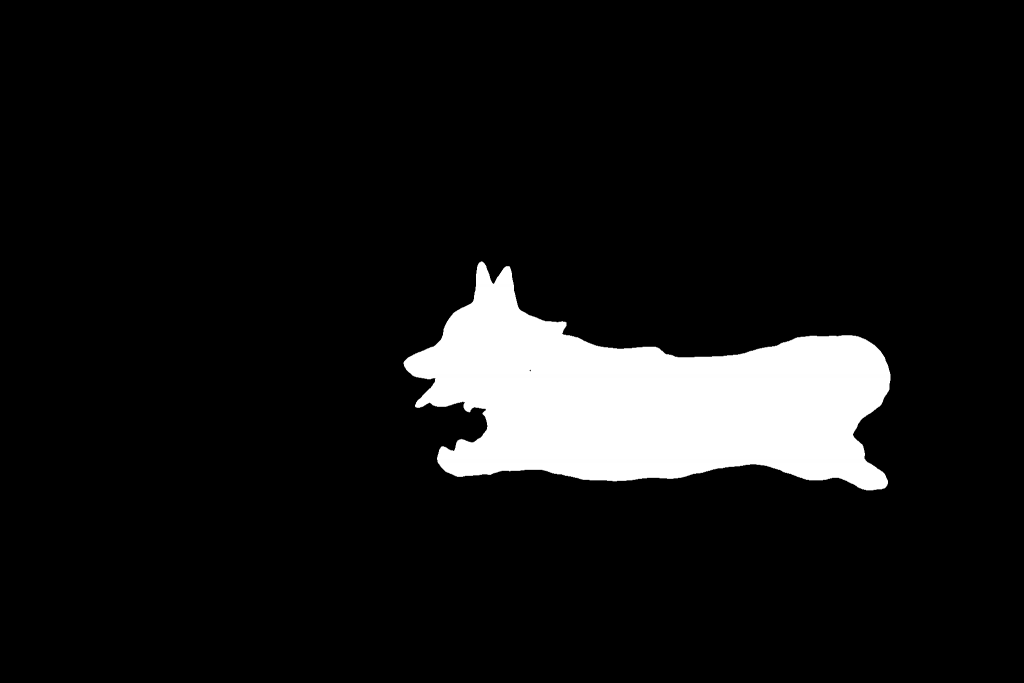
mask = Image.fromarray((np.array(mask.convert('L')) > 0).astype(np.uint8) * 255)为了匹配DAM模型的输入张量的尺寸,上述代码处理后的遮罩图(mask)
# DAM的处理代码
description_generator = dam.get_description(
img,
mask,
query,
streaming=True,
temperature=args.temperature,
top_p=args.top_p,
num_beams=1,
max_new_tokens=512,
)四、实验:用YOLO魔改这篇论文
魔改思路是:用YOLO构造遮罩(Masks),输入DAM进行文本预测。已知YOLOV11官方已经支持分割任务,先下载yolo11x-seg.pt预训练模型(x表示是最大的模型尺寸),大约119M。然后按下面步骤分别实现代码:
步骤一: 定义源图和分类
请输入源图路径:images/2.jpg
请输入目标分类名称:chair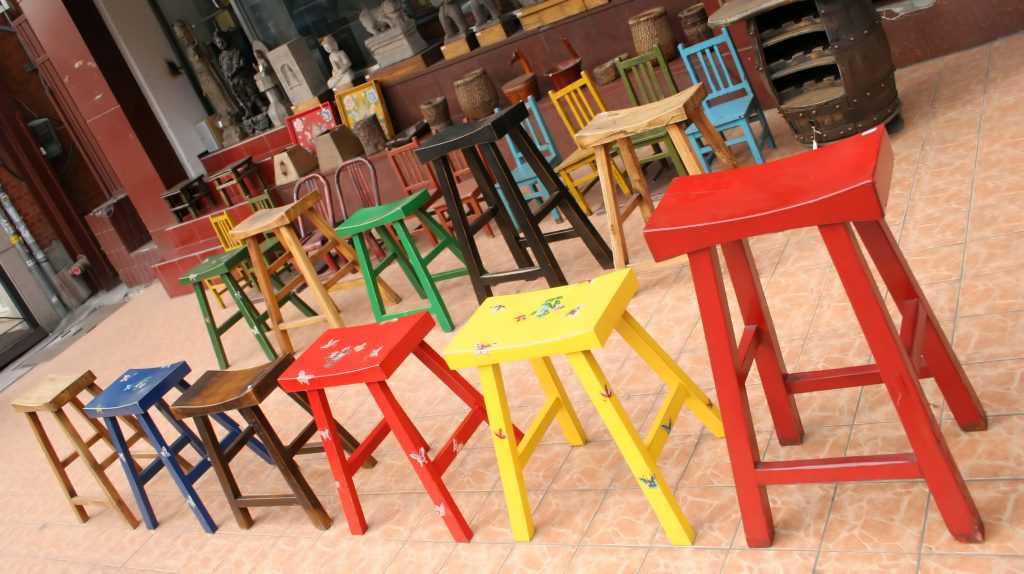
步骤二:调用yolo生成mask
def find_masks(source_path):
"""调用YOLO生成mask并返回路径列表"""
from yolo_seg import generate_masks
# 获取用户输入的class_name
class_name = input("请输入目标分类名称:").strip()
if not class_name:
raise ValueError("分类名称不能为空")
mask_files = generate_masks(source_path, class_name)
return mask_files
步骤三:生成结果:所有Masks的详细描述。
results = generate_mask_descriptions(validated_path, mask_files, output_dir)A collection of colorful stools with various designs. The stools include a red stool with a flat top and four legs, a blue stool with a flat top and four legs, a yellow stool with a flat top and four legs, a green stool with a flat top and four legs, a brown stool with a flat top and four legs, a black stool with a flat top and four legs, and a red stool with a flat top and four legs. Each stool has a unique design and color.
一组色彩丰富、设计各异的凳子。这些凳子包括:一个红色的平顶四腿凳、一个蓝色的平顶四腿凳、一个黄色的平顶四腿凳、一个绿色的平顶四腿凳、一个棕色的平顶四腿凳、一个黑色的平顶四腿凳,以及另一个红色的平顶四腿凳。每张凳子都有其独特的设计和颜色。